What is the ABC of First Aid
In emergencies, every second counts. Knowing the basics of first aid can make the difference between life and death. The ABC of First Aid—Airway, Breathing, and Circulation—is a simple yet powerful guideline that helps you quickly assess and respond to someone in need. Whether it’s a choking incident, a sudden collapse, or severe bleeding, understanding and applying ABC can stabilize the person until professional help arrives. This article will guide you step by step through these essential first aid measures to ensure you’re prepared to act confidently in critical situations.
Introduction to First Aid
Importance of Immediate Response in Emergencies
Quick action can save lives, prevent complications, and reduce the severity of injuries. Even basic first aid knowledge allows you to handle situations like cuts, burns, choking, or sudden illnesses effectively.
Role of ABC in Saving Lives
The ABC of First Aid—Airway, Breathing, and Circulation—provides a simple step-by-step method to assess and assist someone in critical condition. By following ABC, you ensure the person can breathe, receive oxygen, and maintain blood flow, which are essential for survival.
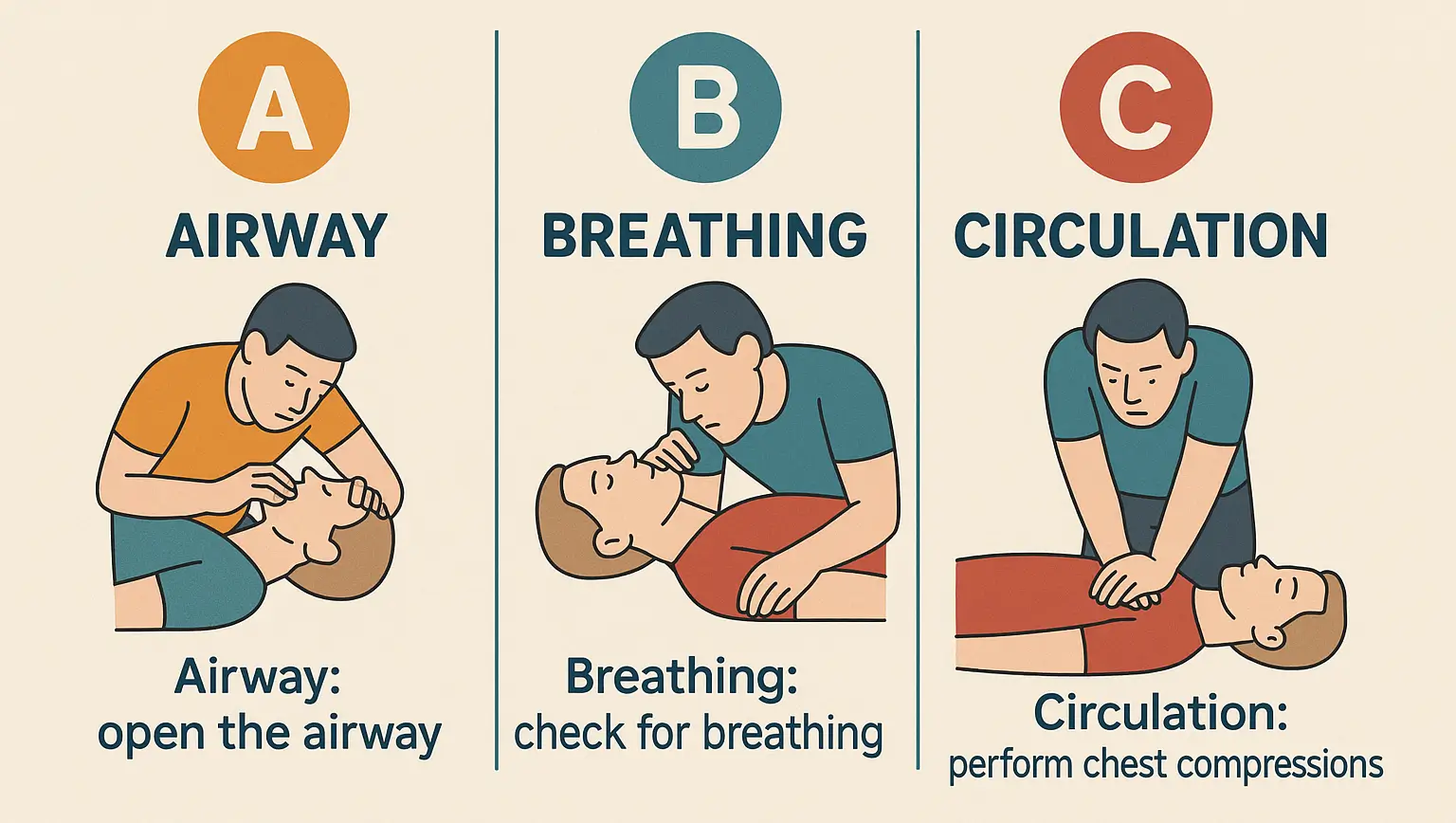
ABC of First Aid
A – Airway
How to check if the airway is clear
- First, make sure the person is lying on their back.
- Gently tilt their head back and lift the chin to open the airway.
- Look inside the mouth for any visible blockage (food, vomit, blood, or tongue falling back).
- Listen for sounds of breathing and feel for airflow from the nose or mouth.
Removing obstructions safely
- If you see a visible object, carefully remove it with a finger sweep (only if you can clearly reach it).
- If the airway is blocked by the tongue, the head-tilt chin-lift or jaw-thrust method can help.
- For unconscious choking, begin abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) or back blows depending on the situation.
- Never blindly poke into the mouth, as this could push the obstruction deeper.
B – Breathing
Checking for normal breathing
- After clearing the airway, check if the person is breathing normally.
- Place your ear close to their mouth and nose for about 10 seconds.
- Look for chest movement, listen for breathing sounds, and feel for air on your cheek.
- If the person is not breathing or only gasping, treat it as no breathing.
Rescue breaths and CPR basics
- If there is no breathing, start CPR immediately.
- Give 30 chest compressions (press hard and fast in the center of the chest, about 5 cm deep, at a rate of 100–120 compressions per minute).
- After 30 compressions, give 2 rescue breaths:
- Tilt the head back, lift the chin, and pinch the nose.
- Seal your mouth over theirs and blow until the chest rises.
- Continue cycles of 30 compressions and 2 breaths until medical help arrives or the person starts breathing normally.
C – Circulation
Checking pulse and controlling severe bleeding
- After checking airway and breathing, assess circulation.
- Feel for a pulse (usually at the carotid artery on the neck, just beside the windpipe).
- If there is a pulse but the person is bleeding heavily, apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage to stop blood loss.
- If bleeding is severe, elevate the injured area (if possible) and use a bandage or tourniquet when necessary.
Initiating CPR if no pulse
- If you cannot feel a pulse within 10 seconds, begin CPR immediately.
- Place the heel of your hand on the center of the chest, with the other hand on top.
- Push hard and fast (5–6 cm deep, 100–120 times per minute).
- Combine with rescue breaths (30 compressions followed by 2 breaths).
- Continue until professional help arrives or signs of circulation return.
Next Steps & Safety Measures
D – Disability
- After airway, breathing, and circulation are stable, check the person’s level of consciousness.
- Use the AVPU scale:
- A – Alert
- V – Responds to Voice
- P – Responds to Pain
- U – Unresponsive
- Look for signs of head injury, spinal injury, or stroke.
- Avoid unnecessary movement if a spinal injury is suspected.
E – Exposure
- Fully assess the person’s body for injuries, bleeding, burns, or fractures.
- Protect them from extreme heat, cold, or rain to prevent shock.
- Keep them covered with a blanket or clothing if cold, but do not overheat.
- Ensure dignity and privacy while checking.
Calling Emergency Services and Preventing Further Harm
- Always call emergency services (ambulance) as early as possible, especially if the person is unresponsive or seriously injured.
- While waiting for help, monitor airway, breathing, and circulation continuously.
- Do not give food or drink to an unconscious person.
- Reassure the patient and keep them safe until professionals arrive.
First Aid: Quick Answers to Common Questions
1. What are the ABC’s in CPR?
The ABC’s in CPR stand for Airway, Breathing, and Circulation.
2. What is the ABC order of first aid?
The order is:
- A – Airway: Make sure the airway is open.
- B – Breathing: Check for normal breathing.
- C – Circulation: Check pulse and control bleeding, start CPR if needed.
3. What is the full meaning of ABC?
In first aid, ABC means Airway, Breathing, Circulation.
4. What is the full form of ABC in safety?
In general safety, ABC means Always Be Careful. In fire safety, it also refers to ABC fire extinguishers (works on Class A, B, and C fires).
5. What is the ABC of first aid kit?
It refers to the basic essentials needed to support Airway, Breathing, and Circulation such as gloves, face shield, rescue mask, bandages, antiseptic, and gauze.
6. Importance of ABC in first aid
ABC focuses on the three life-saving priorities—keeping the airway open, ensuring breathing, and maintaining blood circulation.
7. ABC of first aid PDF
This usually means a downloadable guide explaining Airway, Breathing, and Circulation for study or training purposes.
8. What is the ABC of first aid in order?
- Airway → clear airway
- Breathing → check and support breathing
- Circulation → check pulse, stop bleeding, give CPR if no pulse
9. What is first aid and explain it?
First aid is the immediate care given to someone who is injured or suddenly ill until professional medical help is available.
10. What is the importance of first aid?
It can save lives, reduce pain, prevent conditions from worsening, and promote faster recovery.
11. What are the basics of first aid?
- Assess the situation (safety first)
- Follow ABC (Airway, Breathing, Circulation)
- Control bleeding, treat wounds, burns, or shock
- Call for medical help
12. What is the full meaning of first aid?
First Aid means the first and immediate assistance given to someone suffering from injury or illness before medical treatment is available.
13. What best defines first aid?
First aid is the initial help provided to an injured or ill person until professional care is given.
14. What is the full meaning of aid?
Aid means help, support, or assistance in times of need.
15. 7 steps of first aid
- Assess the situation
- Call for help
- Check responsiveness
- Open airway
- Check breathing
- Give CPR/first aid as needed
- Monitor until help arrives
16. What is the meaning of first aid?
It is the emergency care given immediately to an injured or sick person before a doctor or ambulance arrives.
Learn More: Tea Tree Oil Balm: Natural Relief for Itchy Skin & Rashes


1 Comment
Travel First Aid Pouch Set Review: Compact Emergency Organizer · December 5, 2025 at 10:13 am
[…] medical emergencies is essential for travelers, families, and outdoor enthusiasts. The 4 Pcs Travel First Aid Pouch Set offers a compact, portable solution for organizing essential first aid supplies. Unlike […]